
Most doctors will encourage early leg motion and weight-bearing activity during recovery. After repositioning the fracture, metal plates and screws are used to hold the bone in a correct position while it heals. Other surgical procedures typically involve an incision that allows direct access to the broken portion of bone. This keeps the metal rod and the connected bone held into position until the fracture can properly heal. Then, using titanium screws, the rod is screwed into position at each far end of the femur.

Comminuted fracture common location full#
From the inside, this rod extends through the full length of the bone, including the fractured portion. During this procedure, a long metal rod is inserted into the marrow canal of the femur. The most common method used by orthopedic surgeons is known as intramedullary nailing. Multiple methods might be utilized by your surgeon in repairing a femur fracture, depending on the severity and the type of fracture being operated on. Prior to realigning the fracture, exposed tissue and bone must be thoroughly cleaned and antibiotics are provided to help avoid infection. In the event of an open fracture, surgery is required within 8 hours of the injury.
Comminuted fracture common location skin#
If skin around your fracture is not lacerated, your surgeon will wait until you’re stable before operating. Prior to surgery your doctor will conduct multiple medical history and physical examinations, as well as X-rays and CT scans. To help your doctor diagnose your specific fracture, it’s important that they know the ins and outs of your injury. Fractures that involve portions of other joints and tissue, or in which the broken portion of the bone is displaced from its original position are typically more difficult to repair. Fracture classification is very important to surgeons as treatment difficulty varies depending on the type of break.
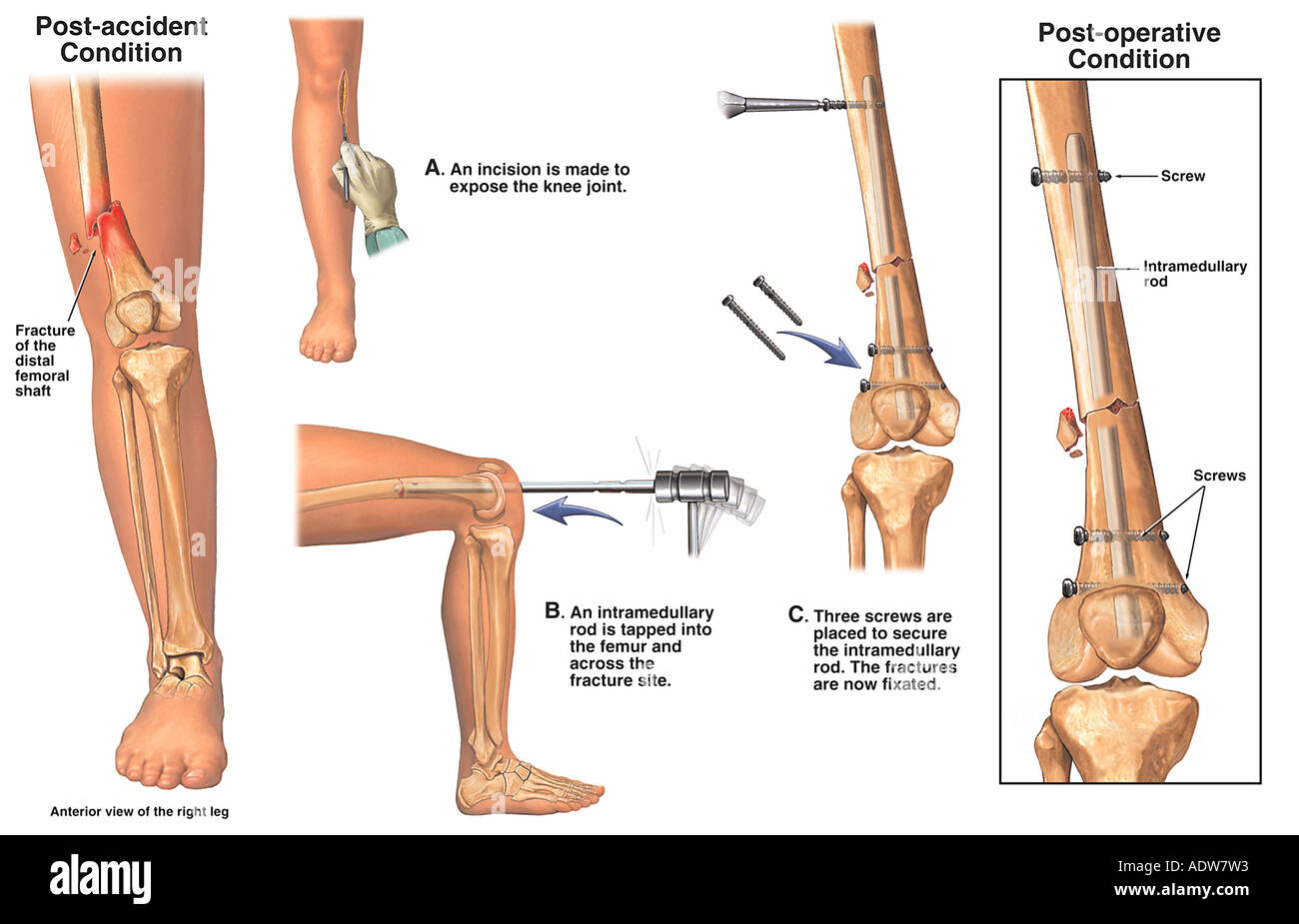
In more serious injuries, the fractured portion of the femur can break the skin (open fracture), or even break into more than two pieces (comminuted fracture). Fractures are then classified based on the breakage pattern, and whether or not skin and muscle tissue has been damaged by the injury. Distal fractures occur near the knee joint, middle fractures occur along the bone’s shaft, and proximal fractures occur near the hip joint. Femur fractures are first classified by their exact position on the bone. Like with most bones, your femur can experience a large variety of fracture types.

High-energy collisions, such as severe falls and motor vehicle crashes are the most commonly seen causes. Because the femur is so strong, it takes a significant amount of force to break it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
